Rewind 15 years back, when you entered a keyword in the Google search Engine, all you got was 10 blue links. From that time to now, the Search Engine Results Page has transformed drastically to accommodate the needs of the users and also maximize profits for the company running it. Google Search has been the most used search engine in the world by a long margin. In 2012, Google had already indexed over 30 trillion web pages, and received 100 billion queries per month.
Google’s algorithm to rank websites has changed consistently, with minor tweaks done to it upwards of 500 times a year. The major updates like Panda, Penguin and Hummingbird also have had a major impact on the SERPs. Moving from organic search results to paid search results to knowledge graph, RankBrain and answer boxes; organic search has come a long way over these years. Let’s walk through all the changes that have happened and explore what is yet to come:
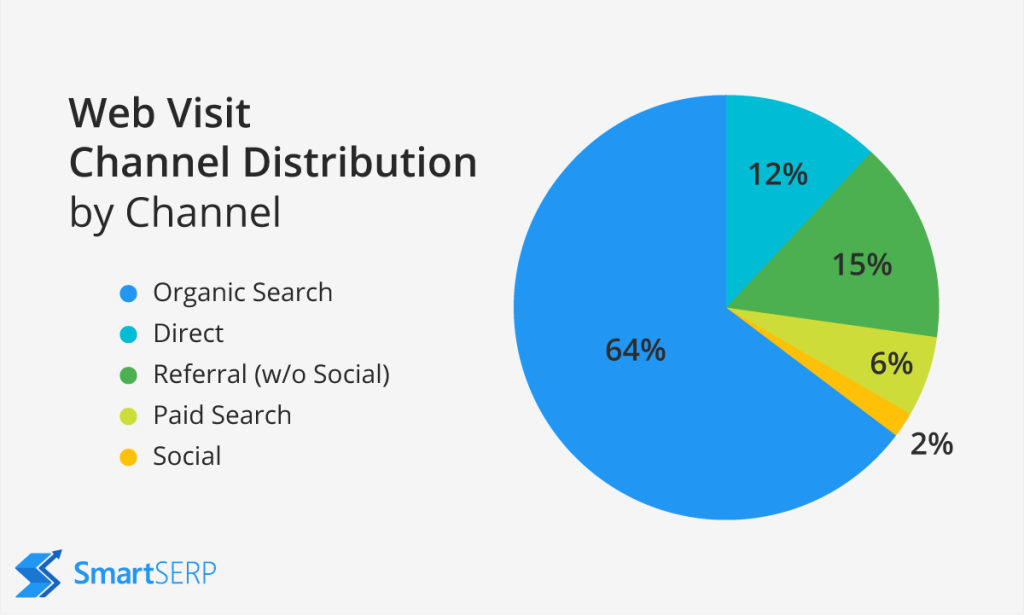
Why is Organic Search so Important?
With the rise of social media and the presence of paid search ads, organic search still holds a very important role in acquiring customers for your business/website. It is important to note that organic traffic is from people who are actually are the perfect customers for your services/content. Organic is what people are searching for with intent; the other options may not be the first choice for people. You and I know that approximately 1000’s of people are searching for a particular thing with different keywords each day. So for the sake of User Experience, search engines want to present only the best service/content providers to their users. Also when brands/organizations who are best suited to the needs of the users are on top of the search results, there is a much greater opportunity to create long-term relationships and increase their overall ROI.
According to the findings by Ad network Chitika, there was a significant drop in traffic from Page 1 to Page 2 results. Page 1 results garnered 92 percent of all traffic from the average search, with traffic dropping off by 95 percent for Page 2. That is why there has been a famous joke that has you might have come across, “The best place to hide a dead body is page 2 of Google search results.” So in spite of organizing all the search results using complex algorithms, search engine users hesitate to visit even the page 2 of the SERPs. This behavior has prompted search engines like Google to make drastic changes to the way they present their SERPs.

How Organic Search has transformed?
When search engines first started out, their goal was just to help users find the most relevant search results. Google used an algorithm called PageRank to decide the order in which the SERPs should be listed. But soon, people figured out how the Google algorithm ranked a web page. They started stuffing their websites with keywords, excessive tagging and linking to optimize their websites and rank better on Google. They were successful in getting their blogs and websites to rank this way.
Google became aware of this trend in the year 2003, and started punishing those website owners who broke its rules, which were mentioned in the webmaster guidelines. At this time, Google also started the practice of personalizing user’s searches using their history as reference. Then came the advent of quality content as the main pillar of Search Engine Optimization. Google started promoting ways in which users could optimize their websites to rank better on Google Search.
The Rise of Paid Ads
By early 2000s Google AdWords became popular. Users were often confused between organic search results and paid search results. But according to research, people always trusted the organic search results. This was also evident in the fact that, conversions were low when people visited websites through paid ads compared to organic results.

The Google Algorithm Updates
By the late 2000s, Google had effectively all black-hat and spam-based link-building practices, penalizing participants in link wheels and exchanges and paid linkers. Google made it clear that content marketing was the best way for websites to improve their search rankings. Google has refined what it considers to be “good” content over the years. In the year 2011, it came out with the Panda update that penalized spammy content and keyword stuffing.
After Panda, it was not possible to use gimmicky content-based tactics, such as favoring a high quantity of content while shipping quality. Instead, the websites that ranked high on Google search were the ones that produced the most valuable content for their users. From that point on, quality content was given the highest priority and became the norm in SEO circles.
New Innovations in Search Engine Result Pages
Personalized Results have been the main focus of Google Search for a long time. There has been a strong decision taken by Google to use machine learning, semantics, connections and patterns to ensure that they can improve the user experience in the near future.

Launching Google Local Search
Google started with Local Search back in 2006, but over the years they have gone through a number of minor iterations and changes to the layout (such as the local carousel, and today’s modern “3-pack” layout), but the biggest change that happened to the ranking factors recently was in 2014, with the Pigeon update.
With this update, Google more heavily incorporated traditional web ranking signals into its ranking algorithm, giving well-optimized websites a major edge in local search. Google also boosted the visibility of high-authority directory websites in its search results. More generally, local searches have become more common and more location-specific over the years, due to mobile devices.

The rise of the Knowledge Graph
Another major change in the SERPs is the introduction Google’s Knowledge Graph in the year 2012. The Knowledge Graph attempts to give users direct, concise answers to their queries, often presenting them with a box of information summarizing the information that they would be interested in. This makes it for the user to get the information without having to go to another webpage and hunting for the information.

The Google Answer Box
Google search extracts the answer to few questions and displays it in the form of answer boxes so that users don’t have to open 5-6 links and compare the information. But this takes away the traffic from the other links listed on the page and drives 90% of the traffic to one webpage.

Google Search Shopping Ads
Now Google Search also includes ads with images from different online shopping portals and sometimes the organic results are drowned out because if it.
Rapid growth of Mobile Searches
According to Google, more than 50 percent of search queries globally now come from mobile devices. Mobile devices have exploded in popularity in the last 5 years, and Google has done everything it can to optimize websites for its mobile users. In 2015, mobile queries officially surpassed desktop queries in Google search. Optimizing for mobile has become not only common, but compulsory in today’s times. All websites need to be compatible to mobile screens and tablets; with Google warning of penalizing websites that don’t follow this trend.
Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP)
In 2016, Google integrated results from its Accelerated Mobile Pages project into its search results in the form of a “Top Stories” carousel in mobile results. Recently, Google started displaying links to AMP pages in the main organic search results. Today, Google has 150 million indexed AMP documents in its index.
RankBrain
In 2016, it was revealed that RankBrain now processes every single Google search (that’s at least 63,000 a second) up from barely 15 percent nine months before. But what exactly is RankBrain?
RankBrain is an algorithm learning artificial intelligence system which Google started using in 2015. It helps Google to process search results and provide more relevant search results for users. RankBrain reportedly interprets the user searches to find pages that may not have contained the exact words that were used in the user search query. There are over 200 different ranking factors which make up the ranking algorithm, of which their exact functions in the Google algorithm are not fully disclosed.
What’s the Future of Organic Search
With the numerous changes to the google search engine, including the Knowledge Graph, answer box, RankBrain and AMP; the quality of search results have definitely increased drastically over the years. In the coming years, we can expect the use of AI and machine learning to predict before hand the type of results we would like to see and curating the content we would like to see, therefore improving the user experience and drastically decreasing the time we spend searching.